Learn the latest trends business innovation with the Educational Programe
Learn the latest trends business innovation with the Educational Programe
Identify the range of macro-economic issues currently impacting on the economy of Papua New Guinea and link appropriate
macro-economic management strategies to those issues.
Wages: payments to employees as a return for the provision of labour or human effort to the production process
Wage indexation: the fixation of wages based on inflation. Idea? Employees should receive wages in line with changes in the cost of living.
In essence, a rise in inflation increases cost of living so wages should be increased as well.
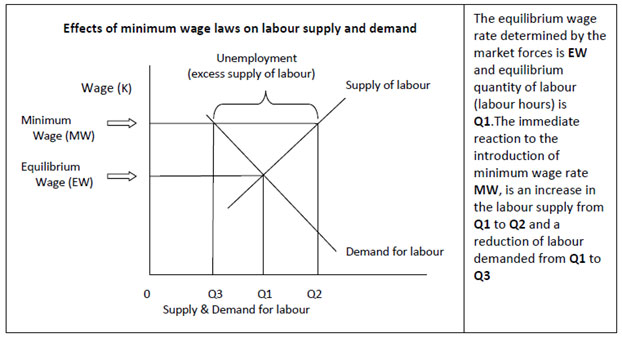
Minimum Wage: the lowest hourly/daily/monthly wage rate that an employer can legally pay to workers – the lowest wage at which workers may sell their labour. The minimum wage does not prevent employees to demand wages above it.
The government may seek to intervene in and modify markets, subject to changing economic and social conditions.
The two main approaches available to government focus around legislation and taxation.
Goods/Services purchased from income are determined by the general price level (inflation). As inflation increases, income earners can purchase fewer items of goods/services unless their wages rise as well.
Organisations that represent workers include:Redistribute income equally through progressive taxation and control cost push inflation
Solve problems of minimum wages between employers and employees